The whole process of carbon fiber SMC molding
Release time:
2025-04-03
SMC (Sheet Molding Compound), carbon fiber SMC is a sheet molding compound formed by impregnating short-cut carbon fiber, matrix resin, and additives at a certain ratio using professional molding and processing equipment according to a certain process.
I. Overview of Carbon Fiber SMC Molding
1. Carbon Fiber SMC
SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) is a sheet molding compound made by impregnating short-cut carbon fiber, matrix resin, and additives in a certain proportion using professional molding equipment and a certain process.

2. Carbon Fiber SMC Molding
This refers to the process of cutting carbon fiber SMC sheets according to the requirements of product size, shape, thickness, and weight, then stacking the cut materials into a heated metal mold cavity, and curing them under pre-set molding conditions;
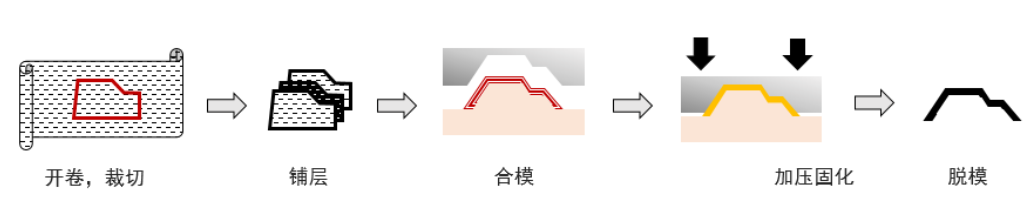
SMC molding has many advantages, such as simple operation, easy automation, short production cycle, ability to mold smooth and complex products with embedded metal parts, and low waste. In addition, products obtained using carbon fiber SMC molding have excellent properties: excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, chemical corrosion resistance, low shrinkage and low water absorption.
II. Carbon Fiber SMC Molding Process
1. Material Inspection
The quality of carbon fiber SMC sheets greatly affects the molding process and product quality. Therefore, before pressing, it is necessary to understand the quality of the material, such as resin type, fiber content, area density and unit weight, film peelability, whether the material is expired, whether the fiber is well impregnated, whether there are impurities, whether the film covering is damaged, material hardness, and uniformity, etc.
2. Material Cutting
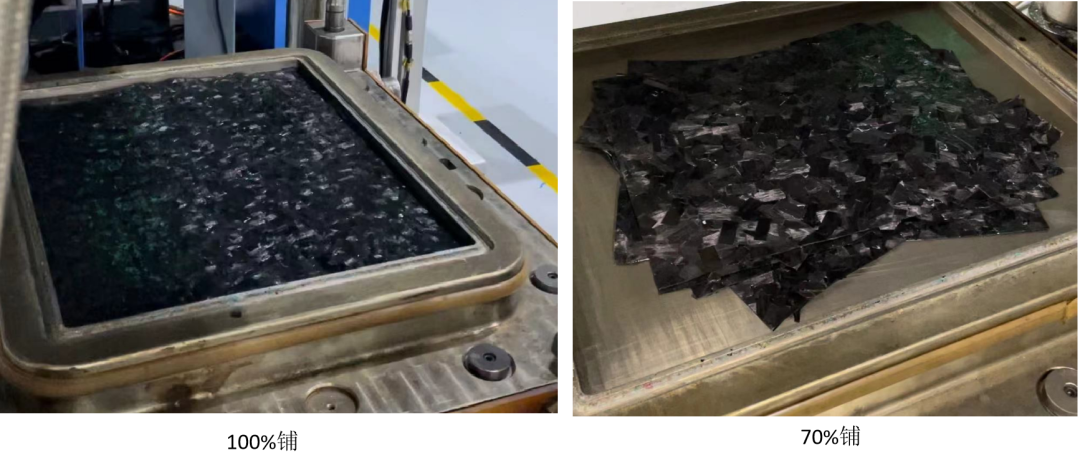
Thaw the material until there is no water mist on the surface of the PE bag before cutting. Cut the sheet according to the structure, material addition position and process of the product. The size is usually 70%-100% of the projected area of the product surface. To prevent contamination by external impurities, remove the upper and lower films before loading, and keep the work area clean to avoid introducing foreign objects.

3. Adjusting Press Parameters
① Mainly includes pressure, temperature, and molding time, which are determined based on product thickness, material requirements, and mold conditions;
② The mold must be installed horizontally and the installation position must be in the center of the press table.
4. Cleaning the Mold
① Thoroughly clean the mold and apply a release agent. Before loading, use a clean gauze to wipe the release agent evenly to avoid affecting the appearance quality of the product. For new molds, they must be degreased before use;
② Close the mold and heat the mold.
5. Confirming Mold Temperature
① Open the mold and measure the upper and lower mold temperatures in the cavity using a contact thermometer (Note: Measure multiple points in the front, back, left, middle, and right to ensure that the surface temperature of the mold reaches the pressing temperature required by the material, and the core temperature is about 5 degrees lower than the cavity temperature);
② If the temperature has not reached, close the mold and wait for continued heating;
③ After the temperature is reached, spray the release agent on the upper and lower molds again.
6. Confirming the Amount and Area of Material Added
① Amount of material added: For the first pressing, the amount of material added for each product can be calculated using the following formula: Amount of material added = Product volume * Density 1.5g/c㎡;
② Material addition area: The size of the material addition area directly affects the density, flow distance and surface quality of the product. It is related to the flow and curing characteristics of SMC, product performance requirements, and mold structure. The material addition area is generally 70%-100%. Too small an area will lead to fiber orientation due to excessive flow length, reduce strength, increase waviness, and even fail to fill the cavity;
③ Material addition position: The material addition position and method directly affect the appearance, strength, and directionality of the product. Under normal circumstances, the material addition position should be in the middle of the cavity. For asymmetric and complex products, the material addition position must ensure that the material flow reaches the ends of the mold cavity simultaneously during molding. 7. High-Temperature High-Pressure Molding
After the material block enters the cavity, start the machine and the press quickly descends. When the upper and lower molds are in contact, slowly apply the required molding pressure. After a period of heat preservation and pressure maintenance, the product molding is complete. During the molding process, the molding process parameters should be reasonably set based on the material characteristics and press conditions.
Molding Temperature: The high and low molding temperature depends on the curing system of the resin paste, product thickness, production efficiency, and complexity of the product structure. The molding temperature must ensure that the initiation and cross-linking reactions of the curing system proceed smoothly and achieve complete curing. The molding temperature of carbon fiber SMC is generally between 130-140℃. Generally speaking, the molding temperature selected for thicker products should be lower than that for thin-walled products to prevent excessive heat accumulation inside the thick product due to excessively high temperatures. Increasing the molding temperature can shorten the corresponding curing time; conversely, when the molding temperature is lowered, the corresponding curing time needs to be extended. The molding temperature should be selected between the highest curing speed and the best molding conditions.
Molding Pressure: The SMC molding pressure varies with the structure, shape, size of the product, and the degree of SMC thickening. Simple-shaped products require less pressure, while complex-shaped products require more pressure. The higher the degree of SMC thickening, the greater the molding pressure required. Products with high appearance and smoothness requirements require higher molding pressure during molding. In short, the determination of the molding pressure should consider multiple factors. Generally speaking, the carbon fiber SMC molding pressure is between 10-25Mpa.
Molding Time: The curing time of carbon fiber SMC at the molding temperature (also called heat preservation time) is related to its properties, curing system, molding temperature, product thickness, and color. The molding time of carbon fiber SMC is usually between 10-15 minutes.
Because SMC is a rapid curing system, the rapid closing of the press is crucial. If the press closes too slowly after the material is added, pre-cured patches may appear on the surface of the product, or there may be material shortages or excessive dimensions. While achieving rapid closure, the mold closing speed should be carefully adjusted at the end of the press stroke. When the mold is a certain distance from closure, the closing speed should be slowed down to facilitate air venting.
8. Demolding and Appearance Inspection
① Slowly open the upper mold. After it rises to 10 mm, check if the product is stuck in the mold. Once it is confirmed that the product remains in the lower mold, the upper mold can be moved to the upper limit position. Open the top mold mechanism and slowly lift to remove the product;
② Inspect the product's appearance for any missing material, dirt, air holes, dry yarn, etc. If the product does not require spraying, simply trim off any excess flash to complete the product production.
Disclaimer: This information is for the exchange and sharing of composite materials expertise and market information only and should not be used for any commercial purposes. If there are any copyright issues or questions about the content, please contact us immediately. We will address them promptly.
Related News

